Difference between revisions of "Oolite JavaScript Reference: Vector3D"
(Updating Oolite scripting documentation for 1.73.) |
(Updating Oolite scripting documentation for 1.73.) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
<small>'''Vector3D''' was called '''Vector''' in Oolite test releases prior to '''1.72'''.</small> |
<small>'''Vector3D''' was called '''Vector''' in Oolite test releases prior to '''1.72'''.</small> |
||
| − | The '''<code> |
+ | The '''<code>Vector3D</code>''' class represents a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vector_%28spatial%29 geometrical vector] in three-dimensional space, in cartesian representation. It is used to represent positions, headings and velocities. Explaining vector geometry is beyond the scope of this document, but there are numerous tutorials on the web. |
=== Vector Expressions === |
=== Vector Expressions === |
||
All Oolite-provided functions which take a vector as an argument may instead be passed an [[Oolite JavaScript Reference: Entity|Entity]] instead, in which case the entity’s <code>[[Oolite JavaScript Reference: Entity#position|position]]</code> is used. In specifications, this is represented by arguments named <code>vectorOrEntity</code>. |
All Oolite-provided functions which take a vector as an argument may instead be passed an [[Oolite JavaScript Reference: Entity|Entity]] instead, in which case the entity’s <code>[[Oolite JavaScript Reference: Entity#position|position]]</code> is used. In specifications, this is represented by arguments named <code>vectorOrEntity</code>. |
||
| − | Additionally, most <code> |
+ | Additionally, most <code>Vector3D</code> methods may be passed three numbers, or an array of three numbers, instead of a vector. In specifications, this is represented by arguments named <code>vectorExpression</code>. For example, if <code>a</code> and <code>b</code> are vectors whose values are (0, 1, 0) and (1, 0, 0) respectively, the following are equivalent: |
var c = a.add(b); |
var c = a.add(b); |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
== Methods == |
== Methods == |
||
=== Constructor === |
=== Constructor === |
||
| − | '''new |
+ | '''new Vector3D'''([value : [[#Vector Expressions|vectorExpression]]]) : Vector3D |
Create a new vector with the specified value. If no value is provided, the vector is initialized to (0, 0, 0). |
Create a new vector with the specified value. If no value is provided, the vector is initialized to (0, 0, 0). |
||
=== <code>add</code> === |
=== <code>add</code> === |
||
| − | function '''add'''(v : [[#Vector Expressions|vectorExpression]]) : |
+ | function '''add'''(v : [[#Vector Expressions|vectorExpression]]) : Vector3D |
Returns the vector sum of the target and <code>v</code>. |
Returns the vector sum of the target and <code>v</code>. |
||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
=== <code>cross</code> === |
=== <code>cross</code> === |
||
| − | function '''cross'''(v : [[#Vector Expressions|vectorExpression]]) : |
+ | function '''cross'''(v : [[#Vector Expressions|vectorExpression]]) : Vector3D |
Returns the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vector_%28spatial%29#Cross_product cross product] of the target and <code>[[#Vector Expressions|vectorExpression]]</code>. |
Returns the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vector_%28spatial%29#Cross_product cross product] of the target and <code>[[#Vector Expressions|vectorExpression]]</code>. |
||
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
=== <code>direction</code> === |
=== <code>direction</code> === |
||
| − | function '''direction'''() : |
+ | function '''direction'''() : Vector3D |
Returns the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unit_vector unit vector] with the same direction as the target. |
Returns the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unit_vector unit vector] with the same direction as the target. |
||
| Line 81: | Line 81: | ||
=== <code>multiply</code> === |
=== <code>multiply</code> === |
||
| − | function '''multiply'''(f : Number) : |
+ | function '''multiply'''(f : Number) : Vector3D |
Returns the product of the target and <code>f</code>. This has the effect of scaling the vector by the factor <code>f</code>. |
Returns the product of the target and <code>f</code>. This has the effect of scaling the vector by the factor <code>f</code>. |
||
=== <code>rotateBy</code> === |
=== <code>rotateBy</code> === |
||
| − | function '''rotateBy'''(q : [[Oolite JavaScript Reference: Quaternion#Quaternion Expressions|quaternionExpression]]) : |
+ | function '''rotateBy'''(q : [[Oolite JavaScript Reference: Quaternion#Quaternion Expressions|quaternionExpression]]) : Vector3D |
Apply the rotation specified by <code>q</code> to the target vector. |
Apply the rotation specified by <code>q</code> to the target vector. |
||
| Line 93: | Line 93: | ||
=== <code>subtract</code> === |
=== <code>subtract</code> === |
||
| − | function '''subtract'''(v : [[#Vector Expressions|vectorExpression]]) : |
+ | function '''subtract'''(v : [[#Vector Expressions|vectorExpression]]) : Vector3D |
Returns the vector difference between the target and <code>v</code>. |
Returns the vector difference between the target and <code>v</code>. |
||
| Line 125: | Line 125: | ||
=== <code>interpolate</code> === |
=== <code>interpolate</code> === |
||
{{Oolite-method-added|1.70}} |
{{Oolite-method-added|1.70}} |
||
| − | function '''interpolate'''(u : [[#Vector Expressions|vectorExpression]], v : [[#Vector Expressions|vectorExpression]], where : Number) : |
+ | function '''interpolate'''(u : [[#Vector Expressions|vectorExpression]], v : [[#Vector Expressions|vectorExpression]], where : Number) : Vector3D |
| − | Returns a point on the line between <code>u</code> and <code>v</code>. If <code>where</code> is 0, the result is <code>u</code>. If <code>where</code> is 1, the result is <code>v</code>. If <code>where</code> is 0.5, the result is half way between <code>u</code> and <code>v</code>. Values of <code>where</code> outside the range [0, 1] are valid; for instance, <code> |
+ | Returns a point on the line between <code>u</code> and <code>v</code>. If <code>where</code> is 0, the result is <code>u</code>. If <code>where</code> is 1, the result is <code>v</code>. If <code>where</code> is 0.5, the result is half way between <code>u</code> and <code>v</code>. Values of <code>where</code> outside the range [0, 1] are valid; for instance, <code>Vector3D.interpolate(u, v, -1)</code> returns a point as far from <code>u</code> as <code>v</code> is, but in the opposite direction. |
| − | <code> |
+ | <code>Vector3D.interpolate(u, v, where)</code> is equivalent to <code>u.[[#add|add]](v.[[#subtract|subtract]](u).[[#multiply|multiply]](where))</code>, or <code>u.[[#multiply|multiply]](1 - where).[[#add|add]](v. [[#multiply|multiply]](where))</code>. |
=== <code>random</code> === |
=== <code>random</code> === |
||
{{Oolite-method-added|1.71}} |
{{Oolite-method-added|1.71}} |
||
| − | function '''random'''([maxLength : Number]) : |
+ | function '''random'''([maxLength : Number]) : Vector3D |
| − | Returns a vector of random length up to <code>maxLength</code>, in a random direction. If <code>maxLength</code> is not specified (or not a number), 1.0 is used. These vectors are uniformly distributed within the unit sphere, which has the effect that longer vectors are more common than shorter ones. Use <code> |
+ | Returns a vector of random length up to <code>maxLength</code>, in a random direction. If <code>maxLength</code> is not specified (or not a number), 1.0 is used. These vectors are uniformly distributed within the unit sphere, which has the effect that longer vectors are more common than shorter ones. Use <code>Vector3D.[[#randomDirectionAndLength|randomDirectionAndLength]]()</code> if an even length distribution is desired. |
In the following image, the cloud on the left was made with the 2D equivalent of <code>random()</code>, and the image on the right was made with the 2D equivalent of <code>randomDirectionAndLength()</code>.<br />[[Image:Randomvectordistribution.png]] |
In the following image, the cloud on the left was made with the 2D equivalent of <code>random()</code>, and the image on the right was made with the 2D equivalent of <code>randomDirectionAndLength()</code>.<br />[[Image:Randomvectordistribution.png]] |
||
| Line 141: | Line 141: | ||
=== <code>randomDirection</code> === |
=== <code>randomDirection</code> === |
||
{{Oolite-method-added|1.71}} |
{{Oolite-method-added|1.71}} |
||
| − | function '''randomDirection'''([scale : Number]) : |
+ | function '''randomDirection'''([scale : Number]) : Vector3D |
Returns a vector of length <code>scale</code>, in a random direction. If <code>scale</code> is not specified (or not a number), 1.0 is used. |
Returns a vector of length <code>scale</code>, in a random direction. If <code>scale</code> is not specified (or not a number), 1.0 is used. |
||
| Line 148: | Line 148: | ||
=== <code>randomDirectionAndLength</code> === |
=== <code>randomDirectionAndLength</code> === |
||
{{Oolite-method-added|1.71}} |
{{Oolite-method-added|1.71}} |
||
| − | function '''randomDirectionAndLength'''([maxLength : Number]) : |
+ | function '''randomDirectionAndLength'''([maxLength : Number]) : Vector3D |
| − | Returns a vector of random length up to <code>maxLength</code>, in a random direction. If <code>maxLength</code> is not specified (or not a number), 1.0 is used. These vectors have a uniform distribution of magnitude (all lengths are equally likely), but cluster towards the origin. Use <code> |
+ | Returns a vector of random length up to <code>maxLength</code>, in a random direction. If <code>maxLength</code> is not specified (or not a number), 1.0 is used. These vectors have a uniform distribution of magnitude (all lengths are equally likely), but cluster towards the origin. Use <code>Vector3D.[[#random|random]]()</code> if an even spacial distribution is desired. |
'''See Also:''' <code>[[#random|random]]()</code>, <code>[[#randomDirection|randomDirection]]()</code> |
'''See Also:''' <code>[[#random|random]]()</code>, <code>[[#randomDirection|randomDirection]]()</code> |
||
Revision as of 20:00, 3 November 2008
Prototype: Object
Subtypes: none
Vector3D was called Vector in Oolite test releases prior to 1.72.
The Vector3D class represents a geometrical vector in three-dimensional space, in cartesian representation. It is used to represent positions, headings and velocities. Explaining vector geometry is beyond the scope of this document, but there are numerous tutorials on the web.
Vector Expressions
All Oolite-provided functions which take a vector as an argument may instead be passed an Entity instead, in which case the entity’s position is used. In specifications, this is represented by arguments named vectorOrEntity.
Additionally, most Vector3D methods may be passed three numbers, or an array of three numbers, instead of a vector. In specifications, this is represented by arguments named vectorExpression. For example, if a and b are vectors whose values are (0, 1, 0) and (1, 0, 0) respectively, the following are equivalent:
var c = a.add(b); var d = a.add(1, 0, 0); var e = a.add([1, 0, 0]); // c, d and e are now all (1, 1, 0).
Properties
x
x : Number (read/write)
The x co-ordinate of the vector.
y
y : Number (read/write)
The y co-ordinate of the vector.
z
z : Number (read/write)
The z co-ordinate of the vector.
Methods
Constructor
new Vector3D([value : vectorExpression]) : Vector3D
Create a new vector with the specified value. If no value is provided, the vector is initialized to (0, 0, 0).
add
function add(v : vectorExpression) : Vector3D
Returns the vector sum of the target and v.
See Also: subtract()
angleTo
function angleTo(v : vectorExpression) : Number
Returns the angle (in radians) between the target and vectorExpression.
v.angleTo(u) is equivalent to Math.acos(v.direction().dot(u.direction())).
cross
function cross(v : vectorExpression) : Vector3D
Returns the cross product of the target and vectorExpression.
See Also: dot()
direction
function direction() : Vector3D
Returns the unit vector with the same direction as the target.
v.direction() is equivalent to v.multiply(1 / v.magnitude()).
See Also: magnitude()
distanceTo
function distanceTo(v : vectorExpression) : Number
Returns the distance between the target and v.
u.distanceTo(v) is equivalent to u.subtract(v).magnitude().
See Also: squaredDistanceTo()
dot
function dot(v : vectorExpression) : Number
Returns the dot product of the target and v.
See Also: cross()
magnitude
function magnitude() : Number
Returns the magnitude (or length) of the vector.
See Also: squaredMagnitude(), direction()
multiply
function multiply(f : Number) : Vector3D
Returns the product of the target and f. This has the effect of scaling the vector by the factor f.
rotateBy
function rotateBy(q : quaternionExpression) : Vector3D
Apply the rotation specified by q to the target vector.
rotationTo
function rotationTo(v : vectorExpression [, maxArc : Number]) : Quaternion
Returns a quaternion corresponding to a rotation from the target vector to v. The optional parameter maxArc specifies a maximum rotation angle; if the angle between the target and v is greater than maxArc radians, a rotation of maxArc radians towards vectorExpression is generated instead.
subtract
function subtract(v : vectorExpression) : Vector3D
Returns the vector difference between the target and v.
See Also: add()
squaredDistanceTo
function squaredDistanceTo(v: vectorExpression) : Number
Returns the square of the distance between the target and v.
u.squaredDistanceTo(v) is equivalent to u.distanceTo(v) * u.distanceTo(v), or u.subtract(v).squaredMagnitude().
squaredMagnitude
function squaredMagnitude() : Number
Returns the square of the magnitude of the vector.
v.squaredMagnitude() is equivalent to v.magnitude() * v.magnitude().
toArray
This method was added in Oolite test release 1.70.
function toArray() : Array
Returns an array of the vector’s components, in the order [x, y, z]. v.toArray() is equivalent to [v.x, v.y, v.z].
tripleProduct
function tripleProduct(v : vectorExpression, w : vectorExpression) : Number
Returns the triple product of the target, v and w.
u.tripleProduct(v, w) is equivalent to u.dot(v.cross(w)).
Static methods
interpolate
This method was added in Oolite test release 1.70.
function interpolate(u : vectorExpression, v : vectorExpression, where : Number) : Vector3D
Returns a point on the line between u and v. If where is 0, the result is u. If where is 1, the result is v. If where is 0.5, the result is half way between u and v. Values of where outside the range [0, 1] are valid; for instance, Vector3D.interpolate(u, v, -1) returns a point as far from u as v is, but in the opposite direction.
Vector3D.interpolate(u, v, where) is equivalent to u.add(v.subtract(u).multiply(where)), or u.multiply(1 - where).add(v. multiply(where)).
random
This method was added in Oolite test release 1.71.
function random([maxLength : Number]) : Vector3D
Returns a vector of random length up to maxLength, in a random direction. If maxLength is not specified (or not a number), 1.0 is used. These vectors are uniformly distributed within the unit sphere, which has the effect that longer vectors are more common than shorter ones. Use Vector3D.randomDirectionAndLength() if an even length distribution is desired.
In the following image, the cloud on the left was made with the 2D equivalent of random(), and the image on the right was made with the 2D equivalent of randomDirectionAndLength().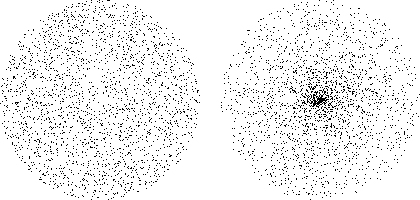
See Also: randomDirection(), randomDirectionAndLength()
randomDirection
This method was added in Oolite test release 1.71.
function randomDirection([scale : Number]) : Vector3D
Returns a vector of length scale, in a random direction. If scale is not specified (or not a number), 1.0 is used.
See Also: random(), randomDirectionAndLength()
randomDirectionAndLength
This method was added in Oolite test release 1.71.
function randomDirectionAndLength([maxLength : Number]) : Vector3D
Returns a vector of random length up to maxLength, in a random direction. If maxLength is not specified (or not a number), 1.0 is used. These vectors have a uniform distribution of magnitude (all lengths are equally likely), but cluster towards the origin. Use Vector3D.random() if an even spacial distribution is desired.
See Also: random(), randomDirection()